
Practical metrology fundamentals: instruments, uncertainty, inspection methods, and concise examples engineers can use in labs and on the shop floor.
Continue reading Metrology basics
Practical metrology fundamentals: instruments, uncertainty, inspection methods, and concise examples engineers can use in labs and on the shop floor.
Continue reading Metrology basics
A pressure sensor converts pressure into an electrical signal for control and monitoring, while a pressure gauge provides a direct visual reading. Both serve different roles, depending on accuracy and application needs.
Continue reading Pressure Sensor vs Pressure Gauge
A Coordinate Measuring Machine delivers traceable precision. It verifies GD&T, controls measurement uncertainty, and supports fast, repeatable dimensional inspection. This guide blends data, field practice, and clear procedures for real engineering work.
Continue reading Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM Basic Guide for Engineers)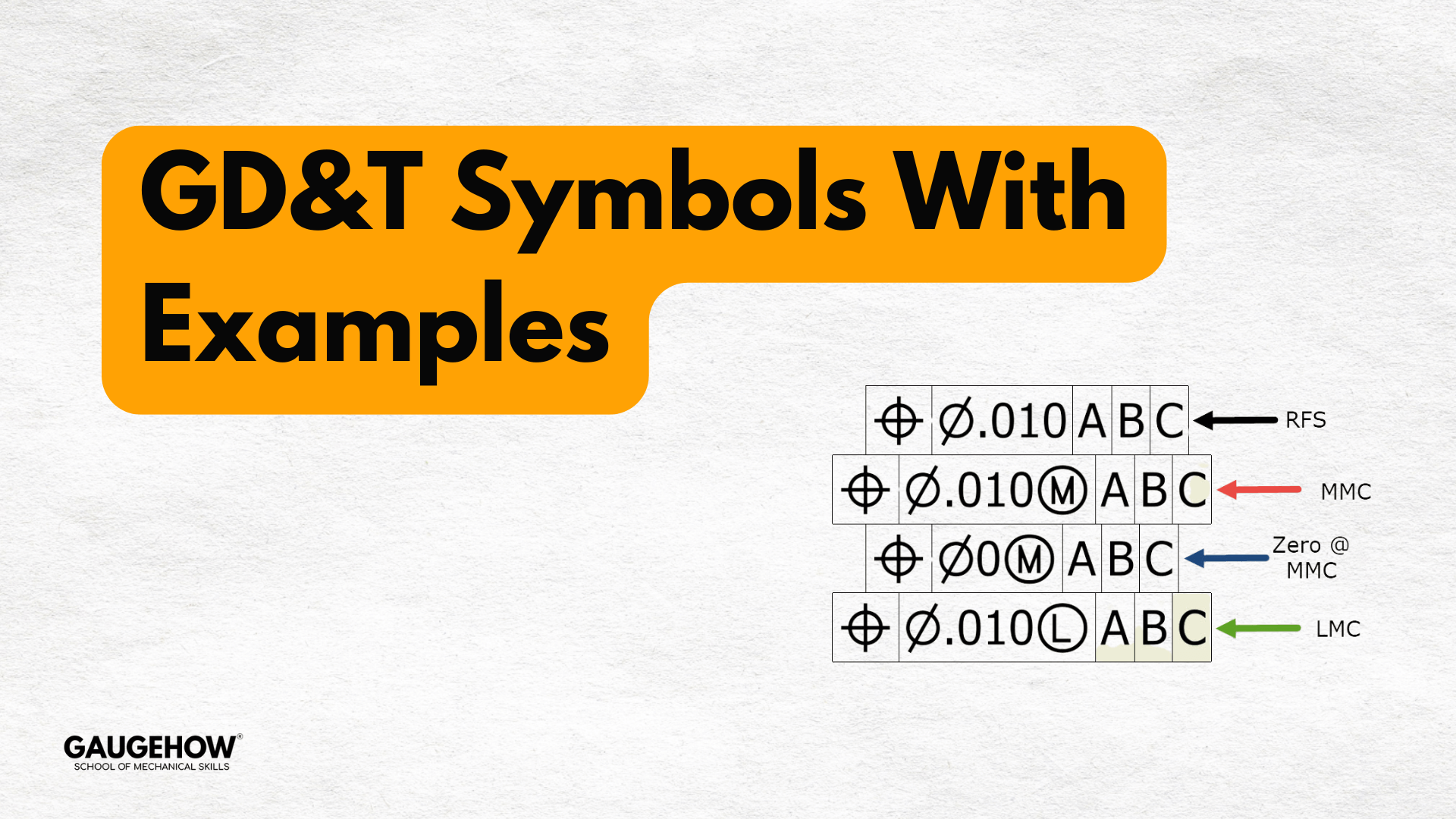
GD&T symbols with examples define geometric tolerances — shape, orientation, location, and runout — and show practical callouts (Position, Flatness, Profile, Circularity) that ensure part function.
Continue reading GD&T Symbols With Examples